Noise Reference & Settings
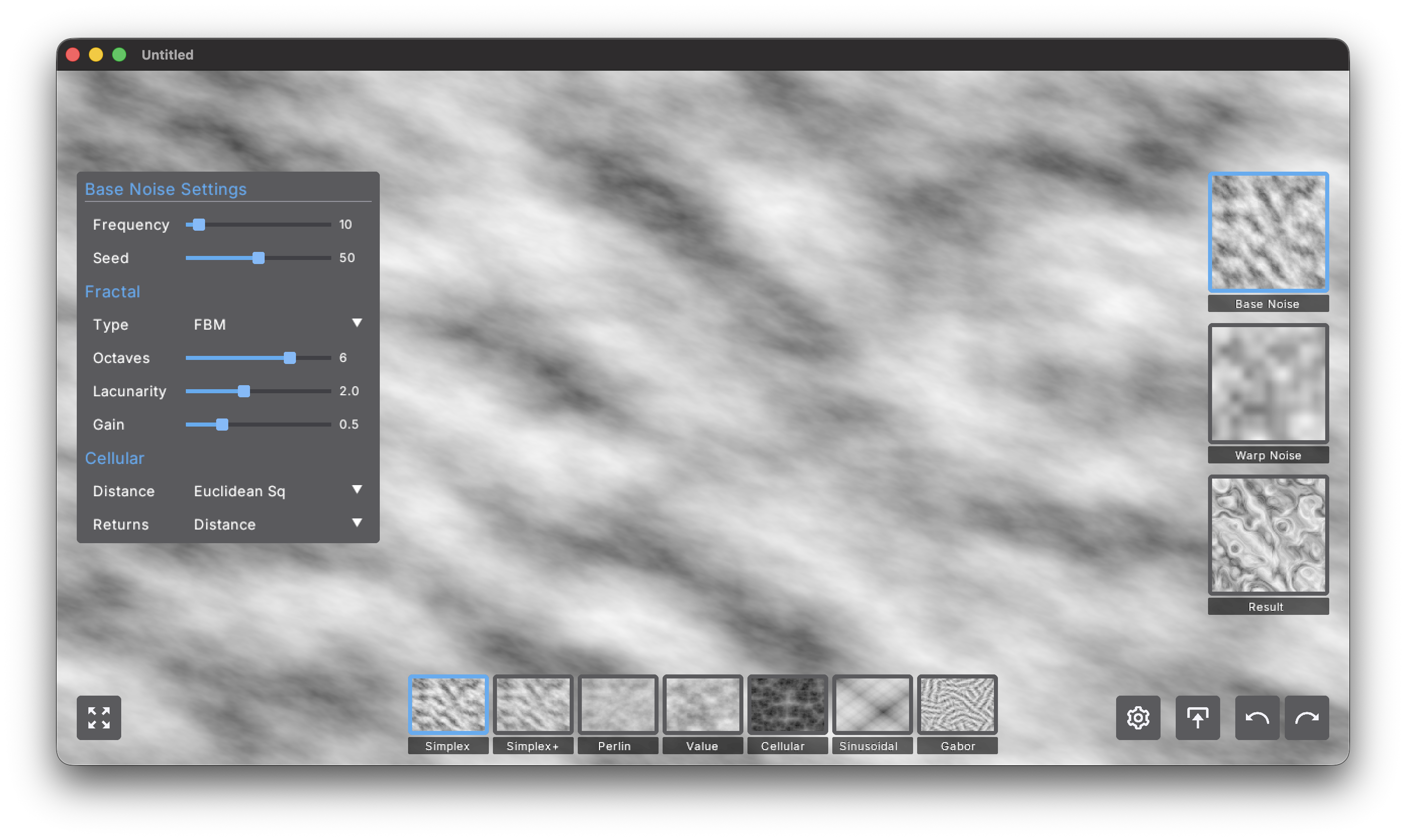
Denrim: Noise supports three layers of noise, displayed on the right side of the UI:
- Base Noise
- Warp Noise
- and the rendering Result
When the Base Noise or Warp Noise is selected, you can apply one of the available noises to that layer. The available noises are:
- OpenSimplex 2 (displayed as OpenSimplex). Modern smooth gradient noise with minimal artifacts for general organic textures.
- OpenSimplex 2S (OS2S) (displayed as OpenSimplex+). Variant of OpenSimplex with a slightly different frequency response for a touch more detail.
- Perlin. Classic gradient noise with gentle structure, great for natural-looking patterns and legacy compatibility.
- Value. Interpolated random values that produce blockier, retro-style noise at low frequencies.
- Cellular (Voronoi). Cell-based patterns that excel at stone, cracks, or organic blobs.
- Sinusoidal. Layered sine waves for rhythmic, wavy patterns and subtle fabric-like textures.
- Gabor. Oriented, band-limited noise ideal for directional grain, brush strokes, or stylized hatching.
Each of these noises supports the following settings which are displayed on the left side:
General Noise Settings
- Fequency (1-100). Frequency controls how tight or loose the pattern is: higher values pack more detail into the same space (smaller features), while lower values spread the pattern out (larger, smoother shapes).
- Seed (0-100). Seed is the random starting point for a noise field; changing it reshuffles the pattern without altering any of your other settings, so you can explore variations with the same look and scale.
- Octaves (1-8). Stack multiple noise layers at different scales. More octaves = more detail, but 4-6 usually gives the best natural look.
- Lacunarity (1.0-4.0). How much the frequency increases each octave. Default 2.0 doubles the frequency - higher values create more contrast between scales.
- Gain (0.0-1.0). How much each octave's amplitude decreases. Default 0.5 creates balanced detail - lower values make fine details subtle, higher makes them prominent.
Fractal Types
- FBM. Standard layering, natural results, use for most cases
- Ridged. Inverts and sharpens the noise into mountain ridges and lightning bolts
- Ping Pong. Creates unusual oscillating patterns, great for alien/experimental looks
Cellular Settings
These only apply to the Cellular noise.
- Distance (Euclidean, Euclidean Sq, Manhattan, Hybrid). Chooses how cell boundaries are measured — Euclidean gives soft circular cells, Euclidean Squared exaggerates edges, Manhattan produces diamond / rectilinear patterns, and Hybrid blends styles for a more varied look.
- Returns (Cell Value, Distance, Distance 2). Selects what the cellular noise outputs — cell value gives classic Voronoi “cells,” distance gives smooth boundary maps, and distance 2 uses the second-nearest point for layered or outline-like effects.
When any of the noise settings change, the thumbnails for all noises and layers automatically adjust to the new settings.
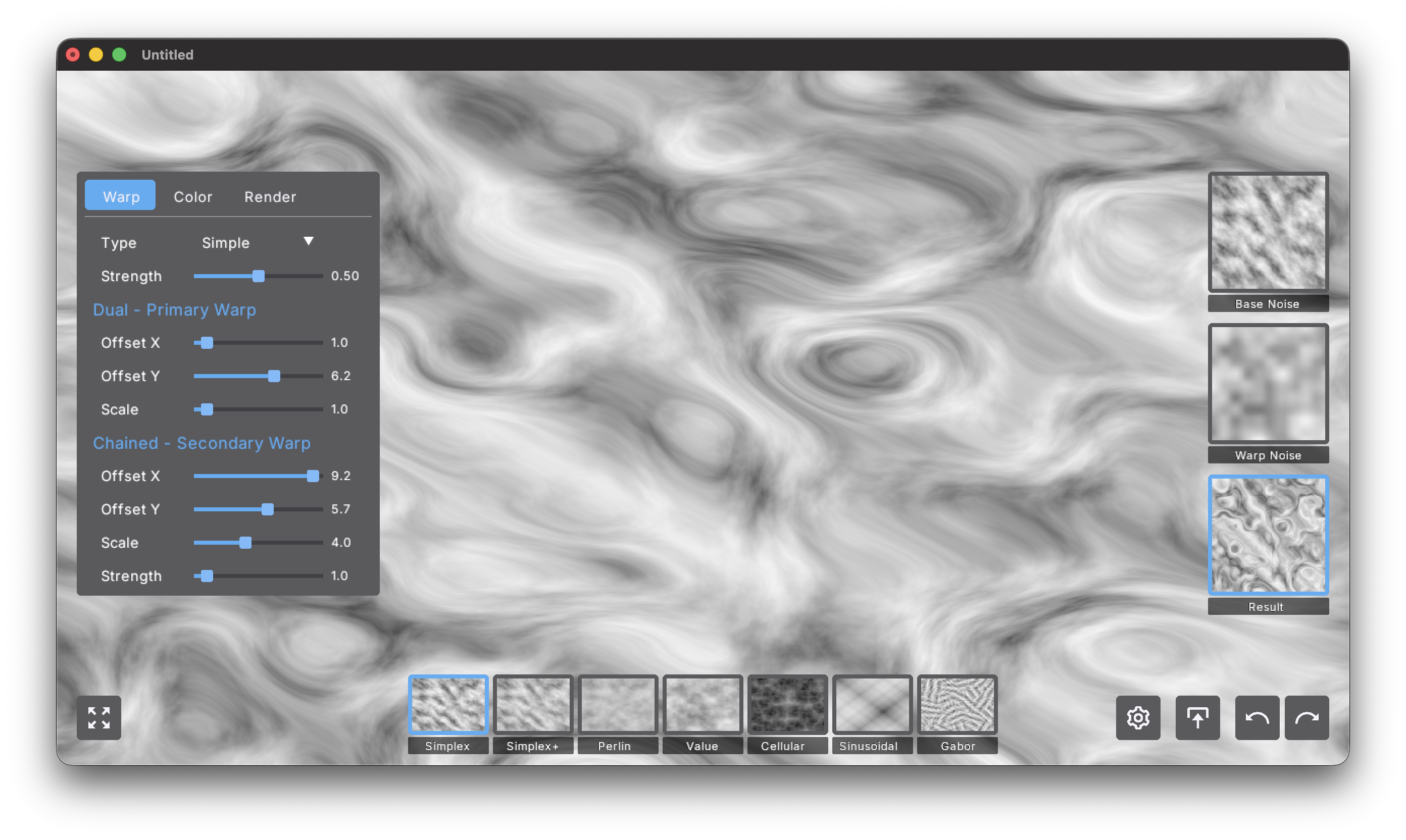
When the Result layer is selected, the Warp, Color, and Render settings are displayed.
Warp Settings
Domain warping distorts the base noise using the warp noise layer, creating flowing organic patterns impossible with basic noise alone.
-
Type (Simple, Dual, Chained). Chooses the warping algorithm:
- Simple: Single-pass warp using one noise offset
- Dual: Two sequential warp passes for compound distortions
- Chained: The warp noise itself is warped before distorting the base (most organic)
-
Warp Strength (0.0-1.0). Controls the overall intensity of the warp effect. Start at 0.5 for subtle flow, go to 1.0 for dramatic swirls.
For more information, see the Warp Formulas page.
Dual - Primary Warp
- Offset X / Y (0.0-10.0). Shifts where the warp noise is sampled. Change these to get completely different warp patterns without affecting other settings.
- Scale (0.1-5.0). The frequency of the warp noise itself. Lower values (0.5-1.5) create large sweeping flows, higher values (2.0-5.0) produce fine detailed warps.
Chained - Secondary Warp
Only active in Dual and Chained modes.
- Offset X / Y (0.0-10.0). Independent offset for the second warp layer, creates layered compound effects.
- Scale (0.1-5.0). Frequency of the second warp. Use a different scale than primary for best results — try primary at 1.0 and secondary at 3.0.
- Strength (0.0-2.0). How much the secondary warp contributes. In Dual mode, this controls the second warp pass intensity. In Chained mode, this controls how much the pre-warp distorts the main warp.
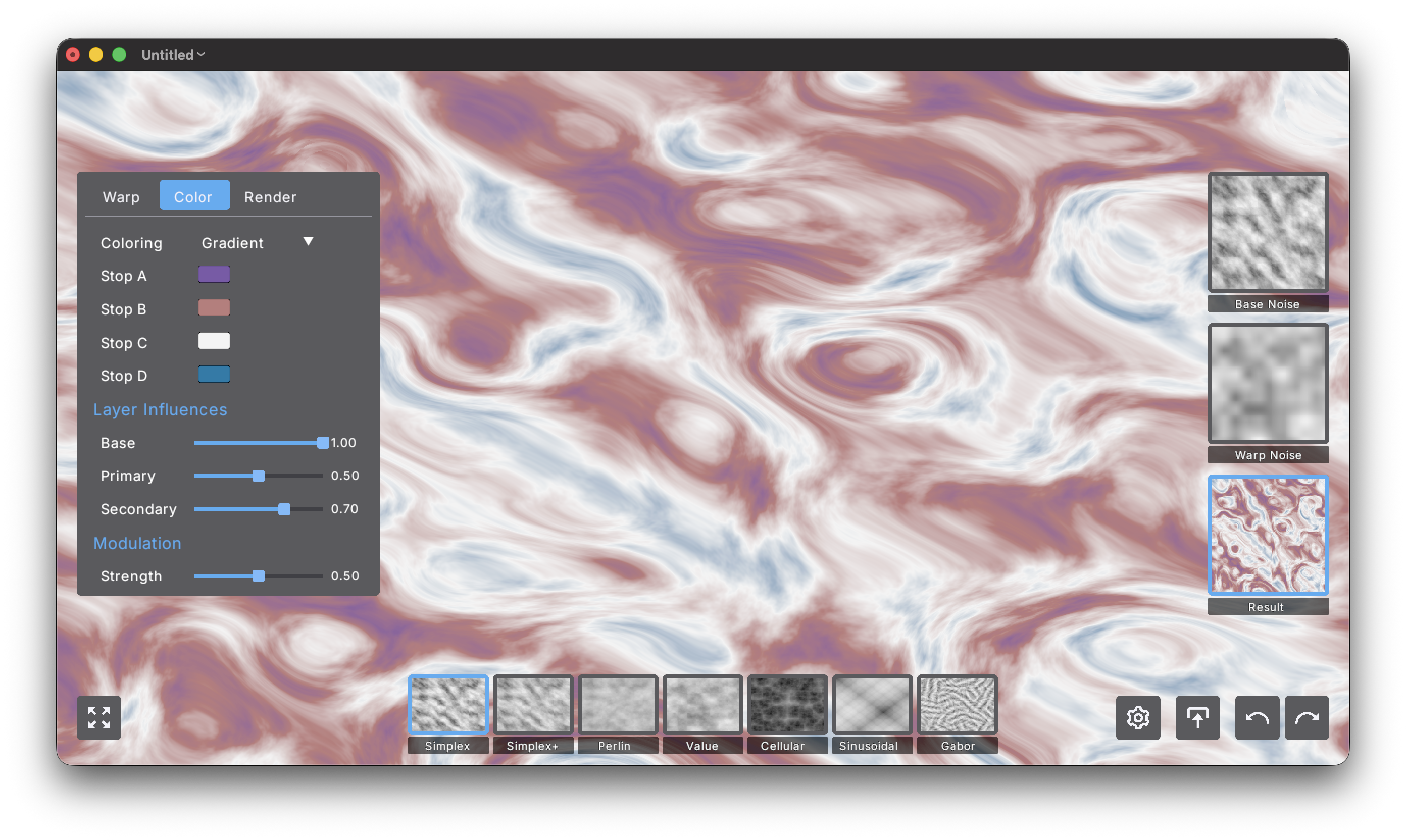
Color Settings
Transform noise into vibrant patterns using the color system.
- Coloring (Grayscale, Gradient, Layered, Modulated). Chooses the coloring mode:
- Grayscale: Pure black-to-white based on noise value
- Gradient: Smooth 4-color gradient mapping
- Layered: Colors influenced by separate noise layers
- Modulated: Color variation modulated by secondary patterns
Color Stops
Click any color button to open the color wheel and define your palette.
- Stop A - Maps to darkest noise values (0.0)
- Stop B - Maps to dark-mid tones (0.33)
- Stop C - Maps to light-mid tones (0.66)
- Stop D - Maps to brightest noise values (1.0)
The gradient smoothly interpolates between these four colors based on the noise value.
Layer Influences
Control how much each noise layer contributes to the final coloring.
- Base (0.0-1.0). Contribution of the base noise layer. At 1.0 the base noise fully influences colors, at 0.0 it's invisible.
- Primary (0.0-1.0). Weight of the primary warp layer in the color calculation. Higher values let the warp pattern show through more.
- Secondary (0.0-1.0). Weight of the secondary warp layer. Fine-tunes how multiple warp passes affect the final color.
Modulation
- Strength (0.0-1.0). Controls variation in color intensity across the pattern. Higher values create more dynamic, less uniform coloring where the color gradient position varies spatially.
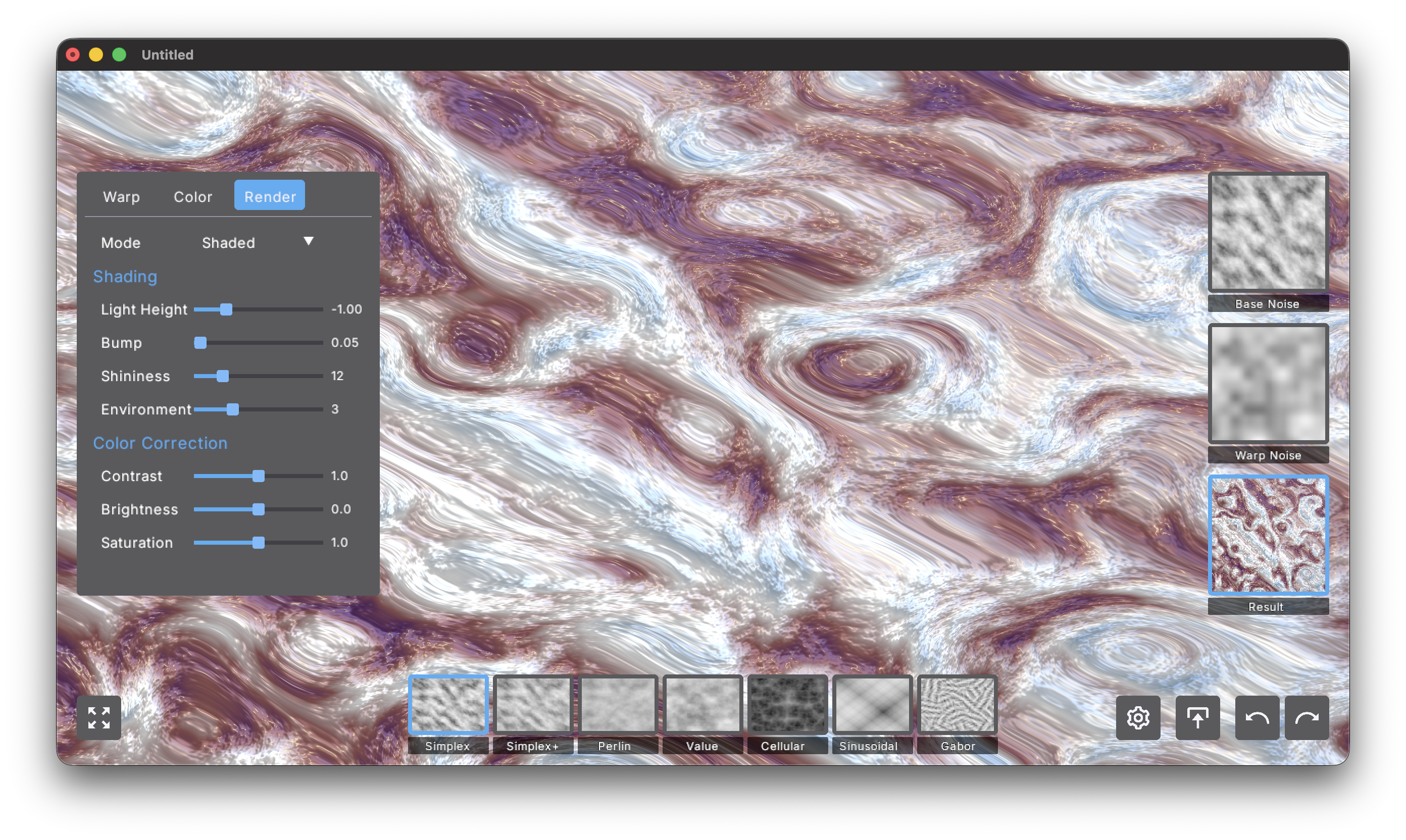
Render Settings
Control how your noise pattern is visualized with rendering modes and post-processing effects.
- Mode (Flat, Plateau, Shaded). Chooses the rendering mode:
- Flat: Pure 2D colored output with no depth or lighting effects
- Plateau: Quantizes noise into 4 discrete elevation bands, creating a topographic map effect
- Shaded: 3D bump-mapped surface with realistic lighting and material properties
Shading
These controls affect the Shaded render mode.
-
Light Height (-2.0-2.0). Vertical position of the light source above the surface. Negative values place the light below (unusual, artistic effects). Lower values create dramatic side lighting with long shadows, higher values produce flatter overhead illumination. Default around 1.0 provides balanced lighting.
-
Bump (0.0-1.0). How much the noise values affect surface height in bump mapping. At 0.0 the surface is completely flat. Low values (0.05-0.15) create subtle texture, moderate values (0.2-0.5) show clear relief, and high values (0.6-1.0) produce extreme exaggerated depth.
-
Shininess (1.0-50.0). Surface reflectivity - controls the size of specular highlights. Note: Higher values create smaller, tighter highlights (less shiny, more matte). Low values (5-10) give metallic glossy appearance with large soft highlights, moderate values (15-25) provide balanced material look, and high values (35-50) create rough matte surfaces with tiny highlights.
-
Environment (0-10). Selects the ambient lighting environment:
- 0-2: Studio - Neutral balanced lighting
- 3-5: Outdoor - Natural daylight simulation
- 6-8: Sunset - Warm golden atmospheric lighting
- 9-10: Night - Cool dark moody illumination
Color Correction
Post-processing adjustments applied to the final image.
-
Contrast (0.0-2.0). Adjusts the difference between light and dark values. Below 1.0 creates softer, more muted patterns with reduced punch. At 1.0 contrast is unchanged. Above 1.0 increases drama and makes lights lighter and darks darker.
-
Brightness (-1.0-1.0). Shifts the entire image lighter or darker without changing relative differences between values. Negative values darken everything, 0.0 is neutral, positive values brighten. Does not affect contrast, only overall exposure.
-
Saturation (0.0-2.0). Controls color intensity. At 0.0 you get pure grayscale regardless of chosen colors. At 1.0 colors appear natural as specified. Above 1.0 creates oversaturated, vibrant, eye-popping results.
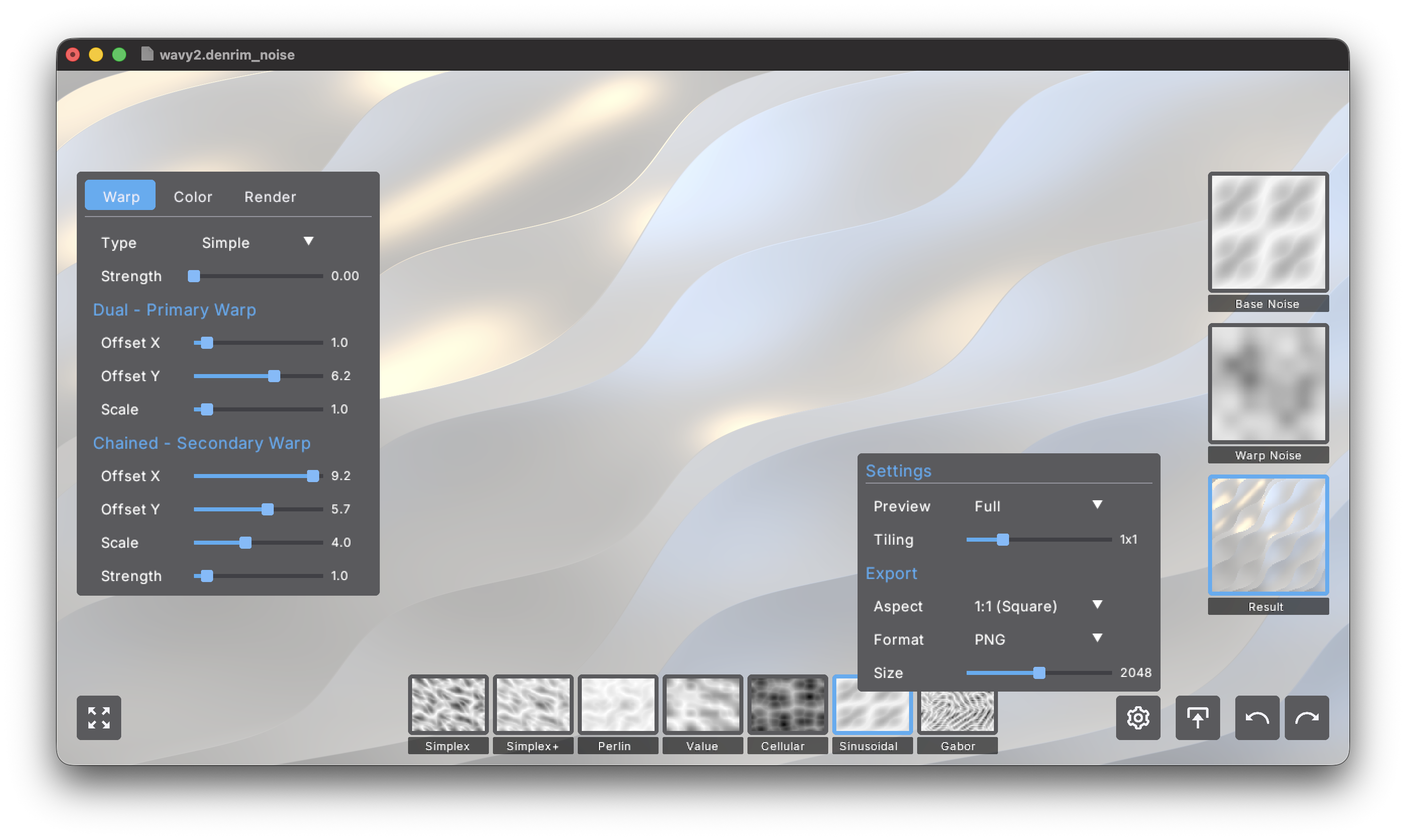
Settings
Configure preview and export options via the Settings panel (accessed through the settings button).
Preview Settings
-
Preview (Full, Square). Controls the preview viewport shape:
- Full: Preview fills the entire window, showing your pattern at the current window aspect ratio
- Square: Preview maintains a 1:1 square aspect ratio regardless of window size
-
Tiling (Off, 1x1, 2x2, 3x3, 4x4). Generates seamless tileable patterns by repeating the noise:
- Off: No tiling, pattern may have seams at edges
- 1x1: Single seamless tile - pattern wraps perfectly when repeated
- 2x2: Shows 2×2 repetition of the tile for verification
- 3x3: Shows 3×3 repetition of the tile
- 4x4: Shows 4×4 repetition of the tile
When tiling is enabled (1x1 or higher), the exported pattern will tile seamlessly - perfect for game textures, 3D materials, and repeating backgrounds.
Export Settings
Configure how your noise is exported when you press the export button.
-
Aspect (1:1 (Square), 16:9 (Wide), 4:3 (Classic), 21:9 (Ultrawide)). Determines the width-to-height ratio of the exported image:
- 1:1: Square output - ideal for game textures and general use
- 16:9: Widescreen format - perfect for desktop wallpapers and modern displays
- 4:3: Classic aspect ratio - good for older displays and print
- 21:9: Ultrawide format - for ultrawide monitors and cinematic compositions
-
Format (PNG, JPEG). Selects the export file format:
- PNG: Lossless compression, larger file size, perfect quality - best for textures and further editing
- JPEG: Lossy compression, smaller file size, good quality - suitable for final wallpapers and web use
-
Size (512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192). The width in pixels of the exported image. Height is calculated based on the selected aspect ratio:
- 512: Small, fast exports for testing
- 1024: Good for game textures and mobile wallpapers
- 2048: High quality for desktop wallpapers and most uses (default)
- 4096: Very high resolution for 4K displays and print
- 8192: Maximum quality for professional use and large prints
Example Export Sizes:
- 2048 at 16:9 → 2048×1152
- 4096 at 1:1 → 4096×4096
- 8192 at 21:9 → 8192×3509
Recommendations:
Game Textures - Aspect: 1:1, Format: PNG, Size: 1024-2048, Tiling: 1x1
Desktop Wallpaper - Aspect: 16:9, Format: PNG or JPEG, Size: 2048-4096
3D Materials - Aspect: 1:1, Format: PNG, Size: 2048-4096, Tiling: 1x1
Web Graphics - Aspect: Any, Format: JPEG, Size: 1024-2048